IoT Gateaway
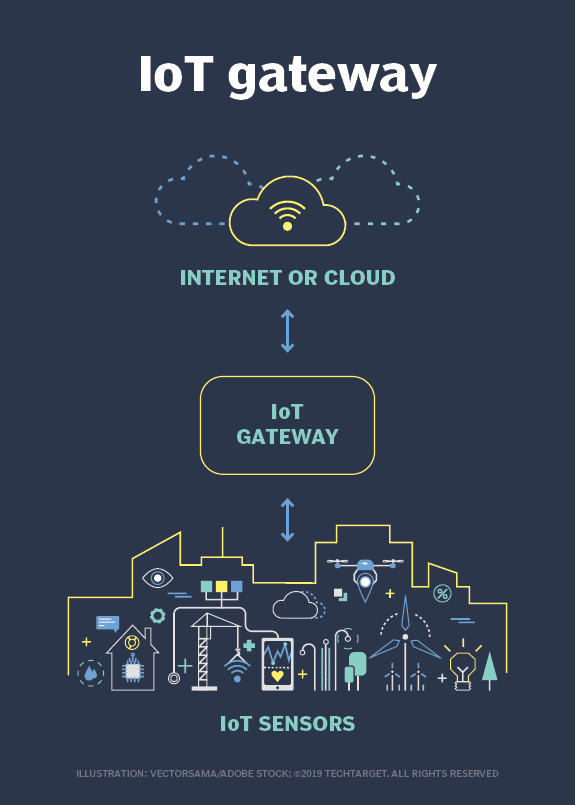
Internet of Things gateway is a crucial component in connecting IoT devices, such as sensors and smart devices, to the cloud. It acts as a bridge between these devices and the cloud, enabling data to be processed and monitored. Whether a physical device or software, an IoT gateway centralizes data flow, allowing businesses to manage their IoT ecosystems more efficiently. In enterprise and consumer applications alike, gateways play a significant role in linking the operational and digital worlds.
Originally, IoT gateways were designed to transfer data in one direction—primarily from devices to the cloud. However, modern gateways handle both inbound and outbound traffic. They can send device data to the cloud while also managing tasks like firmware updates from the cloud back to the devices. Moreover, many gateways now preprocess data locally, reducing the volume of data sent to the cloud. This preprocessing, which includes actions such as data deduplication and aggregation, improves efficiency by cutting down on network bandwidth usage and speeding up response times.
The complexity of IoT gateways goes beyond simple routing. They support a wide variety of communication protocols, such as Bluetooth, Zigbee, and Z-Wave, which allows them to integrate with a diverse set of IoT devices within a network. These gateways also route specific data to appropriate destinations, such as sending industrial sensor data to a cloud database or building security data to a SaaS security portal. Gateways are built to handle scenarios like internet outages by caching data locally and can even scale to manage increasing workloads through failover clustering.
Edge computing is another critical function tied to IoT gateways, particularly when dealing with large volumes of data generated by devices like security cameras. Instead of sending all data to the cloud, edge computing processes data locally, deciding what is important enough to upload. This not only reduces bandwidth but also cuts down on cloud storage costs. For instance, video footage of empty spaces can be filtered out, while relevant footage is sent through the gateway to the cloud.
Security is a major concern for IoT gateways, as IoT ecosystems increase an organization’s vulnerability to cyberattacks. Gateways help mitigate these risks by incorporating security features like encryption, tamper detection, and traffic filtering. To further secure IoT systems, companies are encouraged to use authenticated gateways, perform regular security assessments, and keep software up-to-date. By acting as both a communication hub and security checkpoint, IoT gateways play a critical role in maintaining efficient and safe IoT networks.
source: https://www.techtarget.com/iotagenda/definition/IoT-gateway